by Bioengineer , October 9, 2025 –
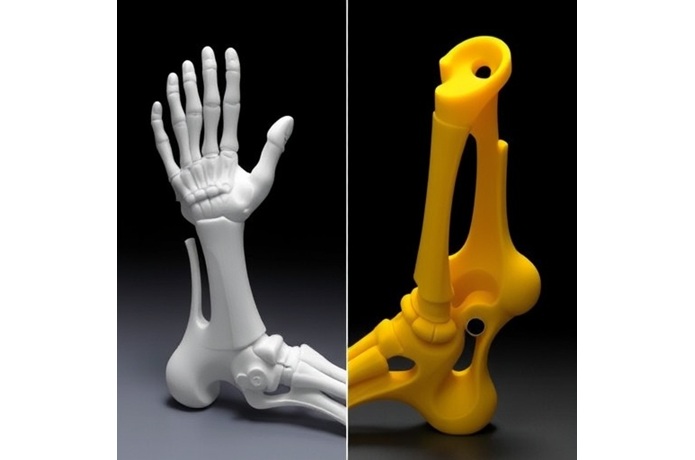
3D printing technology has made remarkable strides in various fields, particularly in medicine and healthcare. A cutting-edge application of this technology is the creation of orthopedic prostheses and orthoses, which play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with limb deficiencies or musculoskeletal disorders. Recent research conducted by Pelczarski et al. signifies a pivotal advancement in this domain, showcasing how 3D printing can revolutionize the fabrication of prosthetic and orthotic devices.
The traditional methods of producing orthopedic devices often involve complex processes that can be time-consuming and costly. Conventional techniques typically require skilled artisans and multiple production steps to create a single prosthesis or orthosis. However, with the emergence of 3D printing, these complexities can be dramatically simplified, allowing for faster and more efficient production. This technology utilizes computer-aided design (CAD) software to create intricate models that are then built layer by layer using various materials.
A key advantage of 3D printing in orthopedic applications is the potential for customization. Each patient has unique anatomical features, which makes a one-size-fits-all approach impractical. Traditional methods often fall short of accommodating individual needs, leading to discomfort and suboptimal functionality. In contrast, 3D printing allows healthcare providers to create bespoke devices that perfectly fit an individual’s specific dimensions, enhancing both comfort and performance. This level of personalization is achieved by integrating advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI or CT scans, into the design phase.
The materials used in 3D printing for orthopedic devices are continually evolving, expanding the possibilities of what can be achieved. From biocompatible plastics to innovative metal alloys, the selection of materials allows for not just functional devices but also lightweight and durable options. This is particularly beneficial for prostheses, where weight is a critical factor in user comfort and mobility. The strength-to-weight ratio can be optimized, leading to devices that are both manageable and robust.